Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are emerging, hot markets. Just do a quick web search and you’ll see the excitement of many organizations looking to adopt these two technologies.
But wait a second: In that quick web search you’ll also see many questions. What’s the difference between RPA and AI? Which technology is better? What do RPA and AI do exactly? And do you have a good understanding of how these two technologies complement each other and provide even more value together, offering new possibilities to your organization than either technology could alone?
Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence 101
Robotic Process Automation is a process automation technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive tasks, manual processes and augment the work of your employee workforce. RPA interacts seamlessly across desktop software, traditional enterprise and browser-based systems and web sites to aggregate data, transform it into actionable information, trigger responses, and communicate with other applications and people to execute repetitive work.
Artificial intelligence describes the actions of machines that mimic the cognitive functions of humans, such as learning and problem solving. AI today comprises a number of technology disciplines, such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP) and many others.
On its own, RPA is really good at automating work that doesn’t require thinking. And AI is really good at thinking and acting like humans. So how do these two work together?
AI-Powered RPA
The ideal next-generation RPA solution uses AI and ML to automate a vast range of high-volume and repetitive tasks that previously required humans to perform. In performing robotic process automation, many think of the RPA software robot as the “arms and legs,” and the AI components as the “brain.”
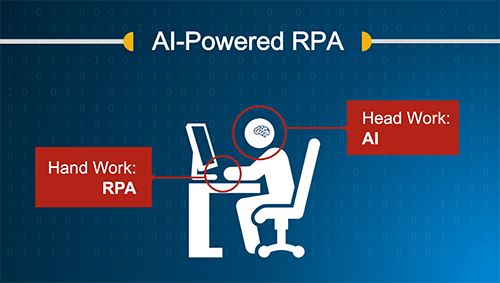
Here are two examples of how incorporating AI into RPA solutions can make the technology even more efficient.
Cognitive Document Automation (CDA): CDA processes structured and unstructured content, especially in business processes that entail the handling of documents. An AI-powered RPA solution can become increasingly efficient over time. As more documents are processed, the solution learns how to intelligently manage variations independently of the channels the information is exchanged through, whether electronic channels like email, web portals or physical paper. CDA delivers the greatest accuracy, efficiency and consistency and dynamically adapts to your evolving processes.
For example, an AI-based RPA solution that includes CDA can recognize the arrival of an invoice, identify which supplier it came from and its associated purchase order, and then trigger an action in the Accounts Payable (AP) system—all without human interaction. Looking one level deeper, CDA relies on AI technologies optical character recognition (OCR), machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP) and some others.
Intelligent Screen Automation (ISA): ISA uses artificial neural network to analyze an image of an application. This is needed, for example, where applications are running on Citrix or other remote desktop environments and only image information is available—there is no direct access to the application and its objects. As virtualization is used almost everywhere, this becomes an increasing issue for an RPA solution to connect and work with environments that only return image information back. ISA addresses this issue by automatically creating user interface objects for the robot designer to use in building the software robot. This results in significantly faster robot development and avoids the issue of screen resolution standardization, because the robot does not depend on screen position to select menu items or buttons when performing tasks.
CDA and ISA are the most-requested AI technologies to be leveraged with RPA, but there are many more. For example, AI services such as Google Vision, IBM Watson or several chatbot services can be easily leveraged by an enterprise-class RPA solution. In those cases, AI is consumed as a service and helps the robots to intelligently perform tasks.
How does it work? One use case is in delivering fast and accurate results in the Know Your Customer compliance process, which is labor-intensive, mundane work being done by highly-skilled analysts. RPA automates that manual “hand” work of collecting information. AI automates the “head” work by analyzing the information provided by RPA and either making a decision or making a recommendation to the human analyst so he or she can make more and faster decisions.
All the excitement around RPA and AI is contagious, but it’s important to have a solid understanding of what the two technologies do separately and how they can be most effectively combined to bring maximum value to your organization. RPA and AI together make up the new smart digital workforce that frees your human workers to be more effective at their work and help to make better decisions.
Up Next: The New Digital Workforce: Robotic Process Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and Humans



